




Program heating techniques include TPD, TPR, TPO, TPS, and TPSR. TPD generally heats up a catalyst that has pre adsorbed a certain gas molecule at a certain rate, while allowing inert gas to pass through at a stable flow rate. When the desorption activation energy of the adsorbed molecules or products on the catalyst surface is reached, they will desorb and be used to study the active sites and distribution of the catalyst.
TPD \ TPR \ TPO \ TPS \ TPSR can be operated using PCA-2200. Please note that the factors affecting the program temperature rise experiment are as follows:
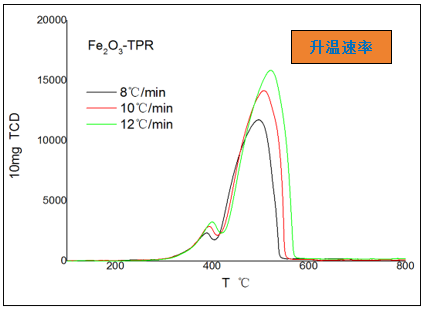
1. Effect of Heating Rate
Excessive heating rate can cause reaction lag and increase the temperature gradient within the sample, making peak separation more difficult and causing significant baseline drift. However, sensitivity can be significantly improved and peak shapes can be clearly observed; Slow heating is more advantageous for the separation of adjacent peaks.
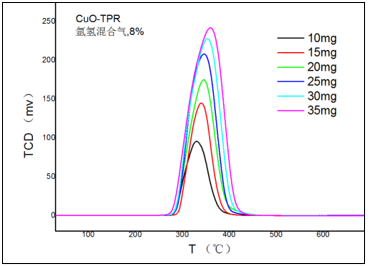
2. How much Sample Should be Used
A small sample size can reduce the temperature gradient within the sample, resulting in more realistic characteristic temperatures, faster diffusion of gas products, and promoting positive chemical equilibrium. Improve the ability to separate adjacent peaks. Appropriately increasing the sample size can improve TCD sensitivity and facilitate the detection of small concentration changes.
3. Selection of Preprocessing Methods
Dynamic atmosphere, static atmosphere, and vacuum are selected reasonably based on the actual reaction simulation needs, combined with kinetic factors. Under static conditions, gas products are difficult to diffuse, resulting in an increase in partial pressure and a shift towards higher temperatures in the reaction; Sensors are prone to contamination. In both cases, the balance room lacks a dry and continuous inert atmosphere protection. Therefore, unless there is a special need, it is recommended to use dynamic blowing.
4. Selection of Carrier Gas
The type of carrier gas affects the concentration detection of the product, and incorrect carrier gas selection can result in loss or reduction of the original signal strength, leading to erroneous analysis. When detecting O2 products, N2 should not be used as the carrier gas, and He should be used instead; When detecting H2, Ar should be used as the optimal carrier gas; Detect CO, CO2, CH4 and complex products, and use He as the carrier gas.

PCA2200 Chemical Adsorption Analyzer and Online Mass Spectrometry Analysis System
contact
Be the first to know about our new product launches, latest blog posts and more.Any question or request?
Click below, we’ll be happy to assist. contact