




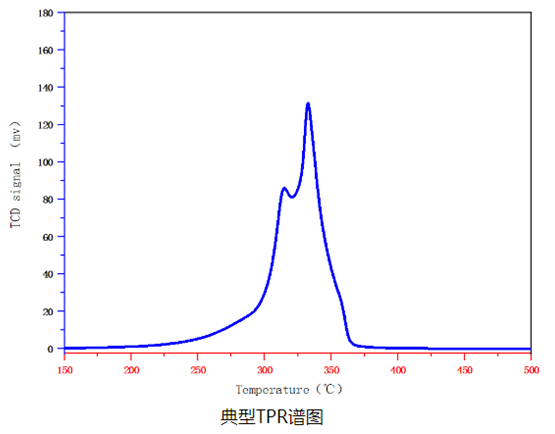
Programmed temperature reduction, abbreviated as TPR, is a catalytic surface mechanism characterization method in programmed temperature analysis, which is one of the important methods for characterizing metal catalysts and transition metal supported catalysts. By testing the reduction temperature of metal oxides, the reduction temperature under pre-treatment conditions of metal catalysts and the upper limit of the usage temperature of metal oxide catalysts can be determined, which can also be used for the study of kinetic reduction activation energy.
The TPR program temperature reduction experiment is usually tested using the Builder PCA1200 chemical adsorption instrument. The usual experimental steps are to introduce low concentration reduction gas (usually low concentration H2 H2 H2/Ar or H2/N2 mixture) from 50-100mg of metal oxides in the reactor, and pass through the catalyst bed at a sequential heating rate of 5 ℃/min to 20 ℃/min. When the hydrogen component is consumed, it will be recorded by the TCD thermal conductivity detector (or mass spectrometry). Each metal oxide has a specific reduction temperature, which is used to characterize the properties of the oxide. The reduction effect can be detected as long as the hydrogen consumption is 1 μ mol.
contact
Be the first to know about our new product launches, latest blog posts and more.Any question or request?
Click below, we’ll be happy to assist. contact