




The BET theory is the name of three scientists (Brunauer Emmett and Teller, abbreviated as BET, derived the multi-layered adsorption formula, also known as the famous BET equation, based on classical statistical theory. They have become the theoretical foundation of particle surface adsorption science and are widely used in the study of particle surface adsorption performance and data processing of related detection instruments.
1. BET equation
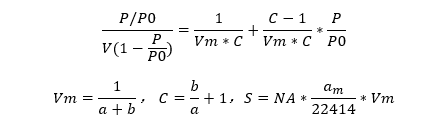
In the formula:
(P/P0)/[V (1-P/P0)]: The ordinate of the BET equation
P/P0: Relative pressure, The abscissa in the BET equation
P0: Saturated vapor pressure of adsorbate at adsorption temperature, KPa
P: Pressure after adsorption equilibrium, KPa
Vm: Single layer saturated adsorption capacity of solid to gas, ml/g
V: The amount of gas adsorbed by a solid at any point of adsorption equilibrium pressure, ml/g
C: Constants related to adsorption and adsorption performance;
a: Fitting the slope of a straight line
b: Fit the intercept of a straight line
S: Specific surface area, m2/g
Am: cross-sectional area of adsorbate molecules, nm2;
NA: Avogadro constant, 6.02 * 10 ^ 23
22414: Volume occupied by 1mol of gas under standard conditions, cm³
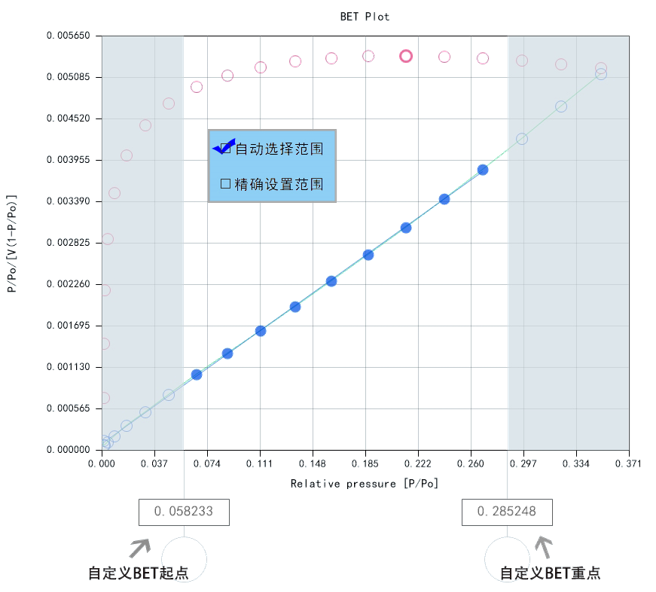
2. Automatic acquisition of BET point range
In data processing systems, BET can automatically obtain or input a range to meet the application needs of different materials.
The automatic selection rule for the relative pressure P/P0 range of BET: The application of the BET equation should be limited to the pressure range within which the relative pressure P/P0 of V * (1-P/P0) continuously increases.
contact
Be the first to know about our new product launches, latest blog posts and more.Any question or request?
Click below, we’ll be happy to assist. contact